Commodore 128 Promo Bundle
Commodore History Part 5 - The C128
| Bezeichung | • Commodore 128 • C128 |
| Jahr | 1985 |
| Prozessor | • Zwei Hauptprozessoren • MOS Technology 8502 mit 2 MHz • Zilog Z80 mit 4 MHz |
| Speicher | • 128 KiB RAM (122 364 Bytes frei) • 72 KiB ROM |
| Anzeige | • 2 Grafik-Chips • MOS Technology 8563 VCD sowie • MOS Technology 8566 VIC-II E (PAL-Version) • MOS Technology 8564 VIC-II E (NTSC-Version) • Text-Darstellung • 40 Zeichen × 25 Zeilen • 80 Zeichen × 25 Zeilen • 80 Zeichen × 50 Zeilen • Grafik-Darstellung • 160 × 200 Punkte, Multicolor Bitmap • 160 × 200 Punkte, Multicolor Bitmap Split-Screen • 320 × 120 Punkte, Standard Bitmap Split-Screen • 320 × 200 Punkte, Standard Bitmap • 640 × 200 Punkte, Hacked-up Mode • 16 Farben |
| Klang | • Klang-Chips • MOS Technology 6581 8-Bit (C128, C128D) • MOS Technology 8580 8-Bit (C128D-CR) • 3 Klangkanäle mit 6 Oktaven • Mono |
| Stromversorgung | externes Netzteil |
| Betriebssystem | modellspezifische Sonderentwicklung |
| Integrierte Programmiersprache | • C64 Modus • Commodore BASIC v2 • C128 Modus • Commodore BASIC v7.0 |
| Anschlüsse / Schnittstellen |
• 1x RF-Out - Standardanschluß • 1x AV-Out - herstellerspezifisch • 1x RGBI Video-Out - DE9 Standardanschluß • 1x Joystick - Standardanschluß • 1x Userport - herstellerspezifisch • 1x Datassette-Schnittstelle - herstellerspezifisch • 1x CBM-Bus für Floppy-Laufwerk / Drucker herstellerspezifisch |
| Slots | 1x Steckmodul-Schacht - herstellerspezifisch |
| Besonderheiten | • Sound-Chip MOS Technology 6581 SID • 3 verschiedene Computer-Modi • C64 Modus • CPU 8501 in 6510 Emulation mit 1 MHz • c128 Modus • CPU 8501 mit 2 MHz • CP/M Modus • CPU Z80 mit 4 MHz • Kompatibel zu Digital Reseach CP/M 2.2 und CP/M 3.0 • Anschluss an den Antenneneingang eines Fernsehers mittels eines mitgelieferten externen HF-Modulators |
| Anmerkungen |

Commodore 128 im CP/M-Modus
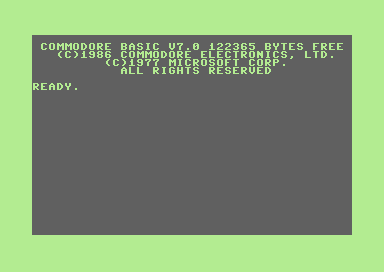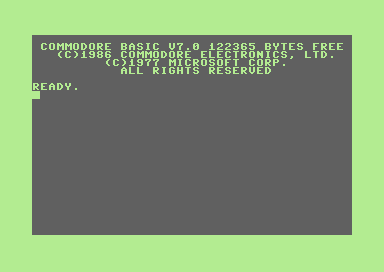
Commodore 128 im BASIC-Modus